Based upon the type of storage to server architecture deployed, storage virtualization software is either built into the operating environment of a storage system, installed on an independent compute system, or available as hypervisor’s capability. There are two types of Server-Storage Architectures being used currently in a Data Center.
Server Centric Architecture
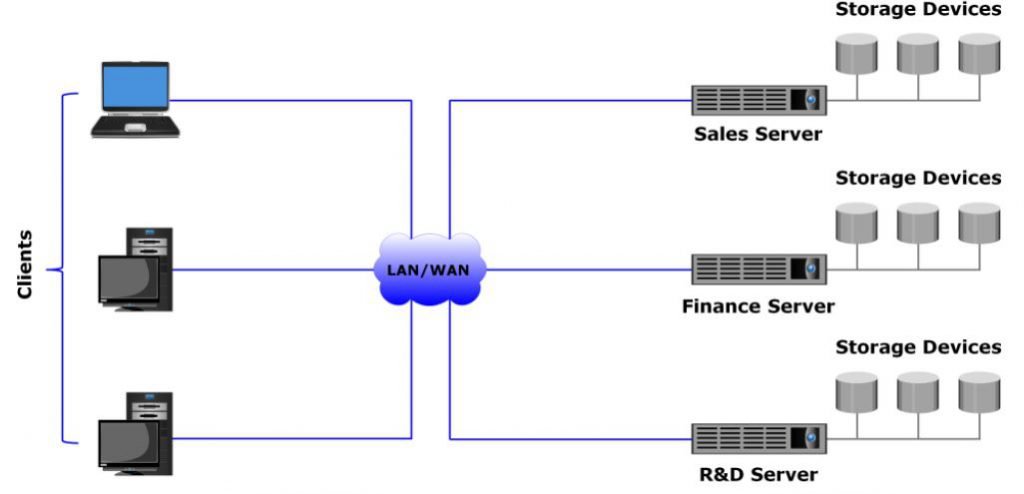
This is a traditional server-storage architecture in which organizations have their own servers running the business applications. Storage devices are connected directly to the servers and are typically internal to the server. These storage devices cannot be shared with any other server. This is called server-centric storage architecture in other words known as Direct Attached Storage (DAS). In this architecture, each server has a limited number of storage devices, and each storage device exists only in relation to the server to which it is connected.
Server-centric architecture has several limitations, and is therefore inadequate to satisfy the growing demand for storage capacity in latest business environments. The number of storage devices that can be connected to one server is limited, and it is not possible to scale the storage capacity.
Advertisement
Moreover, a server cannot directly access the unused storage space available on other servers. A server failure or any administrative tasks, such as maintenance of the server or increasing its storage capacity, also results in unavailability of information.
Information Centric Architecture
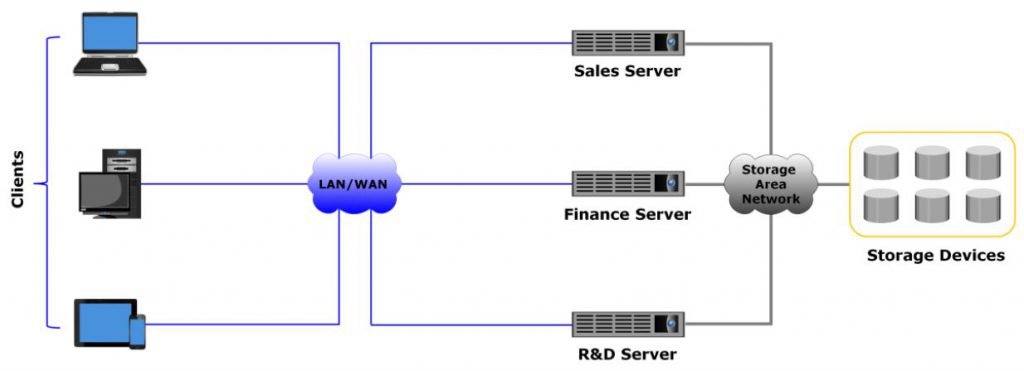
To overcome the challenges of the server-centric architecture, storage evolved to the information-centric architecture. In information-centric architecture, storage devices exist completely independently of servers, and are managed centrally and shared between multiple compute systems. Storage devices assembled within storage systems form a storage pool, and several compute systems access the same storage pool over a specialized, high-speed storage area network (SAN).
A SAN is used for information exchange between compute systems and storage systems, and for connecting storage systems. It enables compute systems to share storage resources, improve the utilization of storage systems, and facilitate centralized storage management. SANs are classified based on protocols they support. Common SAN deployment types are below and are discussed in next posts
- Fibre Channel SAN (FC SAN)
- Internet Protocol SAN (IP SAN)
- Fibre Channel over Ethernet SAN (FCoE SAN)
In this type of architecture, when a new server is deployed in the environment, storage is assigned to the server from the same shared pool of storage devices. The storage capacity can be increased dynamically and without impacting information availability by adding storage devices to the pool. This architecture improves the overall storage capacity utilization, while making management of information and storage more flexible and cost-effective.
Virtualizing the Storage Infrastructure
One primary disadvantage of the above discussed architectures is that we have to login to each storage system to provision or manage the storage to the servers. For example, if an organization is having multiple vendors storage systems, the storage administrator should have multiple storage skills to manage the storage systems.
Also since each vendor has their own interface to manage their storage box, the storage administrator has to know the way to use all the different storage vendors interfaces for managing and monitoring. This increases the complexity of managing the storage in heterogeneous storage environment.
In this fast pace cloud emerging environment, to overcome this complexity and delay in storage provisioning we have a technique called Storage Virtualization which will be discussed in next post.