FC SAN is made up of several physical and logical components. Such as
- Host bus adapters and converged network adapters
- FC Switches and directors
- FC Storage Arrays
- FC Cabling
- FC Fabrics
- FC Name Server
- Zoning
- FC Addressing
- FC Classes and Service
- Virtual SAN
Advertisement
Fibre Channel (FC) SAN Physical Components
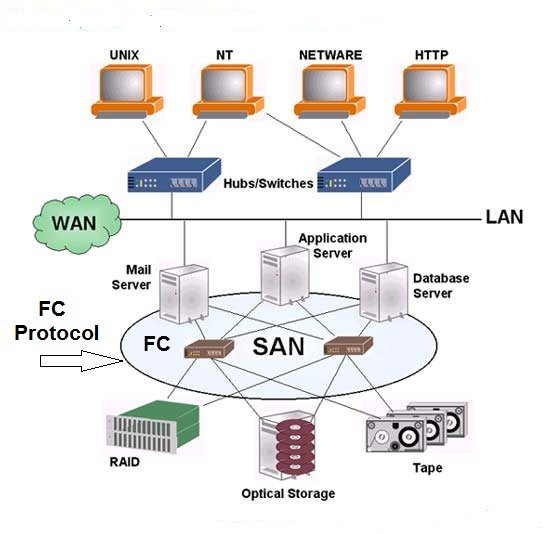
The key FC SAN physical components are network adapters, cables, and interconnecting devices. These components provide the connection network between the storage system and hosts..Here we will see the major physical components to design a Fibre Channel SAN environment.
In an FC SAN, the end devices, such as server or host and storage systems are all referred to as nodes. Each node is a source or destination of information. Each node requires one or more network adapters to provide a physical interface for communicating with other nodes. Hosts and servers connect to the SAN through one or more Fibre Channel host bus adapters (HBA) or converged network adapters (CNA) which are installed on the PCIe bus of the host. Examples of network adapters are FC host bus adapters (HBAs) and storage system front-end adapters.
Hosts interface with the FC SAN via either HBAs or CNAs. These PCI devices appear to the host operating system as SCSI adapters, and any storage volumes presented to the OS via them appear as locally attached SCSI devices. Both types of card also offer hardware offloads for FCP operations, whereas CNA cards also offer hardware offloads of other protocols such as iSCSI and TCP/IP.
Hosts interface with the FC SAN via either HBAs or CNAs. These PCI devices appear to the host operating system as SCSI adapters, and any storage volumes presented to the OS via them appear as locally attached SCSI devices. Both types of card also offer hardware offloads for FCP operations, whereas CNA cards also offer hardware offloads of other protocols such as iSCSI and TCP/IP.
Cables:
FC SAN implementations primarily use optical fiber cabling. Copper cables may be used for shorter distances because it provides acceptable signal-to-noise ratio for distances up to 30 meters. Optical fiber cables carry data in the form of light. There are two types of optical cables: multimode and single-mode.
- Multimode fiber (MMF) cable carries multiple beams of light projected at different angles simultaneously onto the core of the cable. In an MMF transmission, multiple light beams travelling inside the cable tend to disperse and collide. This collision weakens the signal strength after it travels a certain distance – a process known as modal dispersion. Due to modal dispersion, an MMF cable is typically used for short distances, commonly within a data center.
- Single-mode fiber (SMF) carries a single ray of light projected at the center of the core. The small core and the single light wave help to limit modal dispersion. Single-mode provides minimum signal attenuation over maximum distance (up to 10 km). A single-mode cable is used for long-distance cable runs, and the distance usually depends on the power of the laser at the transmitter and the sensitivity of the receiver.
Interconnecting devices:
The commonly used interconnecting devices in FC SANs are FC hubs, FC switches, and FC directors. FC switches and directors provide the connectivity between hosts and storage. Using switches for connectivity offers huge scalability as well as good performance and improved manageability. Switches provide fabric services to help partition the SAN and make it more manageable.
Switches and directors provide connectivity between end devices such as hosts and storage. They operate at layers FC-0, FC-1, and FC-2 and provide full bandwidth between communicating end devices. They also provide various fabric services that simplify management and enable scalability. Also, if multiple FC switches are properly networked together, they merge and form a single common fabric.
- FC HUbs – FC hubs are used as communication devices in Fibre Channel Arbitrated Loop (FC-AL) implementations. Hubs physically connect nodes in a logical loop or a physical star topology. All the nodes must share the loop because data travels through all the connection points. Because of the availability of low-cost and high-performance switches, the FC switches are preferred over the FC hubs in FC SAN deployments.
- FC switch – FC switches are more intelligent than FC hubs and directly route data from one physical port to another. Therefore, the nodes do not share the data path. Instead, each node has a dedicated communication path. The FC switches are commonly available with a fixed port count. Some of the ports can be active for operational purpose and the rest remain unused. The number of active ports can be scaled-up non-disruptively.
- FC Directors – FC directors are high-end switches with a higher port count. A director has a modular architecture and its port count is scaled-up by inserting additional line cards or blades to the director’s chassis. Directors contain redundant components with automated failover capability. Its key components such as switch controllers, blades, power supplies, and fan modules are all hot-swappable. These insure high availability for business critical applications.
The difference between directors and switches is that larger switches, usually with 128 or more ports, are referred to as directors, whereas those with lower port counts are referred to as switches or workgroup switches. Directors have more high-availability (HA) features and more built-in redundancy than smaller workgroup-type switches. For example, director switches can have two control processor cards running in active/passive mode. In the event that the active control processor fails, the standby assumes control and service is maintained. This redundant control processor model also allows for non-disruptive firmware updates. switches do not have this level of redundancy.
Fibre Channel (FC) SAN Logical Components are
Fibre Channel (FC) SAN Logical Components are
- FC Fabrics
- FC Name Server
- Zoning
- FC Addressing
- FC Classes and Service
- Virtual SAN
These components are explained in the next posts in detail
Go To >> Index Page
Sponsored Links




Please tell me how to download this document