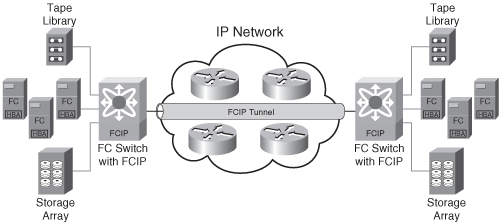
FC SAN provides a high-performance infrastructure for localized data movement. But the organizations are now looking for ways to transport data over a long distance between their disparate FC SANs at multiple geographic locations. One of the best ways to achieve this goal is to interconnect geographically dispersed FC SANs through reliable, high-speed links. This approach involves transporting the FC block data over the IP infrastructure.
Fibre Channel over IP (FCIP) SAN Overview
FCIP is an IP-based protocol that enables distributed FC SAN islands to be interconnected over an existing IP network. In FCIP, FC frames are encapsulated onto the IP payload and transported over an IP network. The FC frames are not altered while transferring over the IP network. In this manner, FCIP creates virtual FC links over IP network to transfer FC data between FC SANs. FCIP is a tunnelling protocol in which FCIP entity such as an FCIP gateway is used to tunnel FC fabrics through an IP network.
The FCIP standard has rapidly gained acceptance as a manageable, cost-effective way to blend the best of the two technologies which are FC SAN and the proven, widely deployed IP infrastructure. As a result, organizations now have a better way to store, protect, and move their data by leveraging investments in their existing IP infrastructure. FCIP is extensively used in disaster recovery implementations in which data is replicated to the storage located at a remote site. It also facilitates data sharing and data collaboration over distance, which is a key requirement for next generation applications.
Advertisement
FCIP Architecture
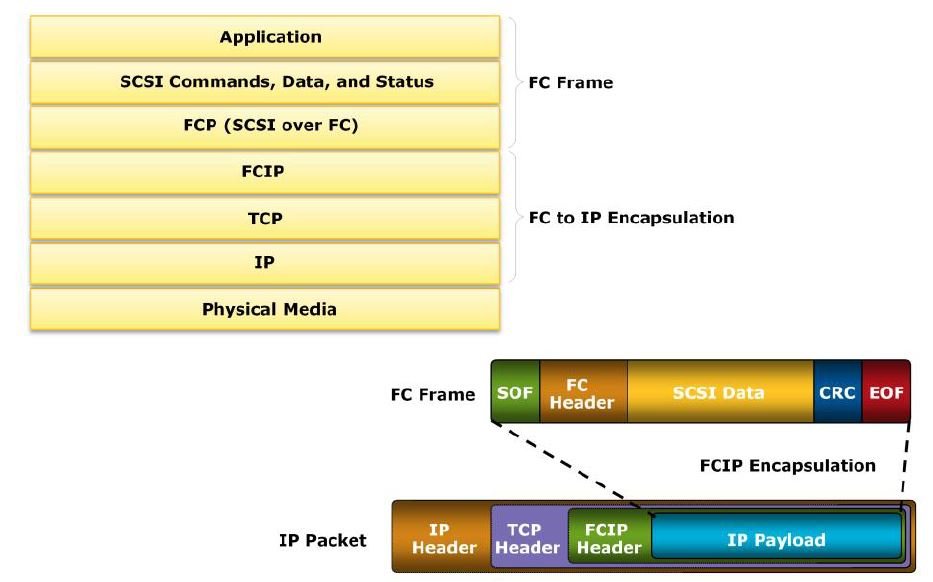
The FCIP protocol stack is shown on the slide. Applications generate SCSI commands and data, which are processed by various layers of the protocol stack. The upper layer protocol SCSI includes the SCSI driver program that executes the read-and-write commands. Below the SCSI layer is the FC protocol (FCP) layer, which is simply an FC frame whose payload is SCSI.
The FC frames can be encapsulated into the IP packet and sent to a remote FC SAN over the IP. The FCIP layer encapsulates the FC frames onto the IP payload and passes them to the TCP layer. TCP and IP are used for transporting the encapsulated information across Ethernet, wireless, or other media that support the TCP/IP traffic.
Encapsulation of FC frame on to IP packet could cause the IP packet to be fragmented when the data link cannot support the maximum transmission unit (MTU) size of an IP packet. When an IP packet is fragmented, the required parts of the header must be copied by all fragments. When a TCP packet is segmented, normal TCP operations are responsible for receiving and re-sequencing the data prior to passing it on to the FC processing portion of the device
FCIP Connectivity Protocol
In an FCIP environment, FCIP entity such as an FCIP gateway is connected to each fabric via a standard FC connection. The FCIP gateway at one end of the IP network encapsulates the FC frames into IP packets. The gateway at the other end removes the IP wrapper and sends the FC data to the adjoined fabric. The fabric treats these gateways as fabric switches. An IP address is assigned to the port on the gateway, which is connected to an IP network. After the IP connectivity is established, the nodes in the two independent fabrics can communicate with other.
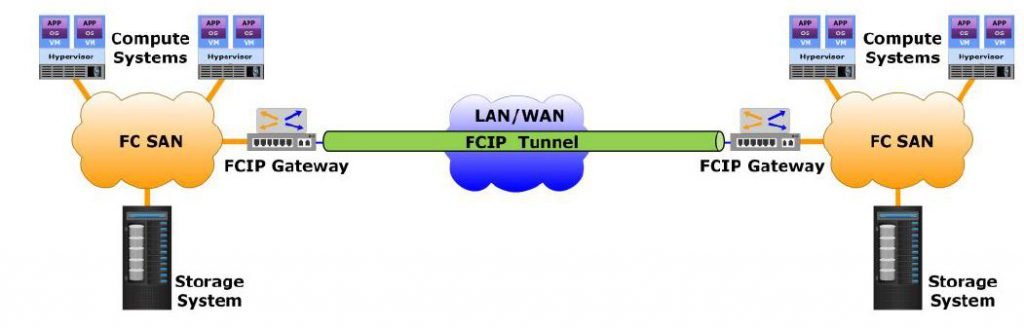
FCIP Tunnel
An FCIP tunnel may be configured to merge interconnected fabrics into a single large fabric. In the merged fabric, FCIP transports existing fabric services across the IP network.
An FCIP tunnel consists of one or more independent connections between two FCIP ports on gateways (tunnel endpoints). Each tunnel transports encapsulated FC frames over a TCP/IP network. The nodes in either fabric are unaware of the existence of the tunnel. Multiple tunnels may be configured between the fabrics based on connectivity requirement. Some implementations allow aggregating FCIP links (tunnels) to increase throughput and to provide link redundancy and load balancing.
Frequently, only a small subset of nodes in either fabric requires connectivity across an FCIP tunnel. Thus, an FCIP tunnel may also use vendor-specific features to route network traffic between specific nodes without merging the fabrics.
A VSAN, similar to a stretched VLAN, may be extended across sites. The FCIP tunnel may use vendor-specific features to transfer multiple VSAN traffic through it. The FCIP tunnel functions as a trunk link and carries tagged FC frames. This allows extending separate VSANs each with their own fabric services, configuration, and set of FC addresses across multiple sites.
Go To >> Index Page