RAID 1+0 is also known as RAID 10 (Ten) or RAID 1/0. RAID 1+0 is also called striped mirror. It is a hybrid of RAID 1 (mirror sets) and RAID 0 (stripe sets). The objective of this RAID type is to combine both striping and mirroring techniques to get both the protection and performance of RAID 0 and RAID 1.
The basic concept of RAID 1+0 is a mirrored pair, which means that data is first mirrored and then both copies of the data are striped across multiple disk drive pairs in a RAID set.
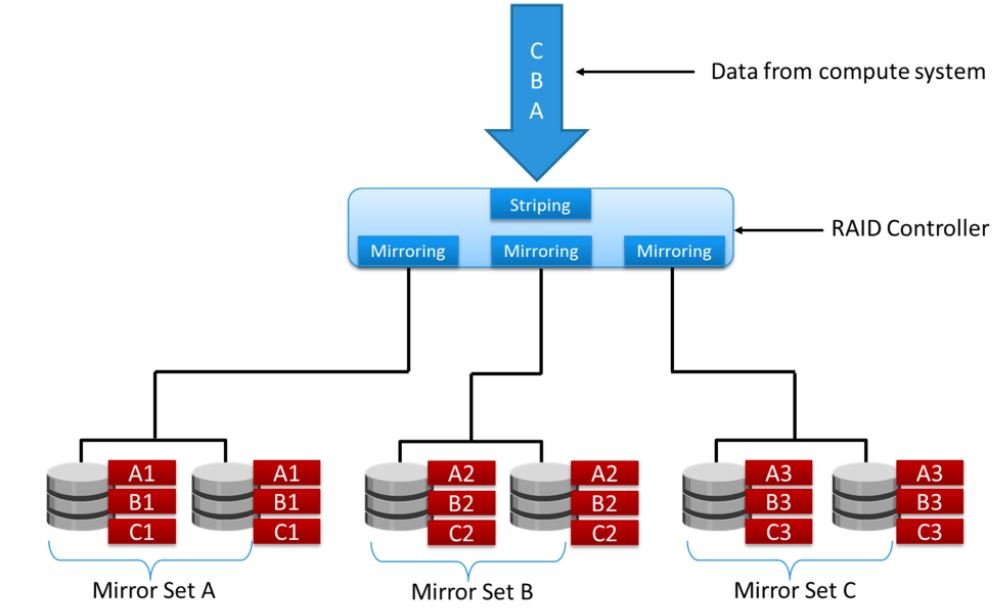
When replacing a failed drive, only the mirror is rebuilt. In other words, the storage system controller uses the surviving drive in the mirrored pair for data recovery and continuous operation.
Data from the surviving disk is copied to the replacement disk. Most data centers require data redundancy and performance from their RAID arrays. RAID 1+0 combines the performance benefits of RAID 0 with the redundancy benefits of RAID 1. It uses mirroring and striping techniques and combines their benefits. This RAID type requires an even number of disks and the minimum is four.
RAID 10 and RAID 01 are not the same, and people often get confused the two . You
always want RAID 10 rather than RAID 01. The technical difference is that RAID 01 first
creates two stripe sets and then creates a mirror between them. The major concern with
RAID 01 is that it is more prone to data loss than RAID 10.
RAID 10 Use Cases
Choose RAID 10 if the capacity overhead can be affordable which comes with RAID 1, then RAID 10 potentially offers the best mix of performance and protection available from the traditional levels.
Advertisement
Advantages
If something goes wrong with one of the disks in a RAID 10 configuration, the rebuild time is very fast since all that is needed is copying all the data from the surviving mirror to a new drive. This can take as little as 30 minutes for drives of 1 TB.
Disadvantages
Half of the storage capacity goes to mirroring, so compared to large RAID 5 or RAID 6 arrays, this is an expensive way to have redundancy.
Go To >> Index Page
Sponsored Links



